Introduction
New York City’s subway system is an iconic part of the city’s infrastructure, serving millions of commuters daily. However, it faces numerous challenges, from outdated technology to frequent delays. In contrast, advanced train systems around the world, such as China’s bullet trains, Japan’s Shinkansen, and Europe’s high-speed rail networks, represent the pinnacle of modern rail technology. This blog will compare the NYC subway to these advanced systems, explore the pros and cons of renovating the subway, and discuss the implications for commuters.

NYC Subway: A Historical Perspective
The NYC subway system, one of the oldest in the world, began operations in 1904. Despite its age, it remains a vital part of the city’s transportation network. However, much of its technology dates back to the 1930s, including electromechanical relays and manual track switching. Efforts to modernize the system have included the introduction of communications-based train control (CBTC) on certain lines, which allows for more efficient train operations.
Advanced Train Systems: Cutting-Edge Technology
China’s Bullet Train: Developed rapidly since the mid-2000s, China’s bullet train system is the world’s largest and most advanced high-speed rail network. Utilizing electrical multiple unit (EMU) train sets, these trains can travel at speeds of up to 380 km/h (236 mph). The system includes the Shanghai Maglev, the world’s first high-speed commercial magnetic levitation line, which reaches speeds of 431 km/h (268 mph).
Japan’s Shinkansen: Known as the “bullet train,” Japan’s Shinkansen network is renowned for its speed, punctuality, and safety. Trains can travel at speeds of up to 320 km/h (200 mph), and the network covers major cities across Japan.
Europe’s High-Speed Rail: Europe boasts an extensive high-speed rail network, with trains like France’s TGV and Germany’s ICE reaching speeds of up to 300 km/h (186 mph). These systems emphasize connectivity between major cities and countries, offering efficient and comfortable travel options.
Pros and Cons of Renovating the NYC Subway
Pros:
- Improved Reliability: Modernizing signals and infrastructure can reduce delays and improve service reliability.
- Enhanced Safety: Upgrading outdated systems can enhance passenger safety, particularly in flood-prone areas.
- Better Commuter Experience: Renovations can lead to cleaner, more comfortable stations and trains.
Cons:
- High Costs: Renovating the subway system is expensive, with estimates reaching $43 billion over five years.
- Disruption: Construction and upgrades can cause significant disruptions to daily commutes.
- Long Timeline: Comprehensive renovations can take decades to complete.
Cost of Renovating the NYC Subway
The cost of renovating the NYC subway is substantial. The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) has outlined a $54 billion plan for improvements over the next five years. This includes modernizing signals, replacing aging subway cars, and upgrading infrastructure to withstand extreme weather. Specific projects, such as the renovation of Chambers Street and 190th Street stations, are expected to cost upwards of $100 million.
Impact on Commuters
Renovating the subway system will have mixed impacts on commuters. On the positive side, improved reliability and safety will enhance the overall commuting experience. However, fare hikes and service disruptions during construction may pose challenges. The introduction of modernized subway cars and expanded lines will ultimately benefit commuters by reducing overcrowding and improving access to underserved areas.
Fare Increases
As part of the financial plan to support these renovations, the MTA has proposed a fare hike that would raise the cost of a single ride to $3 by August 2025. While fare increases can be challenging for commuters, they are often necessary to fund essential upgrades and ensure the system remains safe and reliable.
Insurance Considerations
Insurance plays a crucial role in the renovation process. Flooding and other extreme weather events have exposed vulnerabilities in the subway’s infrastructure
Adequate insurance coverage is essential to mitigate risks associated with these events and ensure financial protection for both the MTA and commuters. Addressing insurance gaps and improving flood risk awareness are vital steps towards urban resilience
Is It Worth It?
The question of whether renovating the NYC subway is worth it depends on one’s perspective. From a long-term viewpoint, the benefits of a modern, reliable, and safe subway system outweigh the costs and disruptions. However, the immediate challenges, including high costs and construction-related inconveniences, cannot be ignored. Ultimately, investing in the subway’s future is crucial for maintaining New York City’s status as a global metropolis.
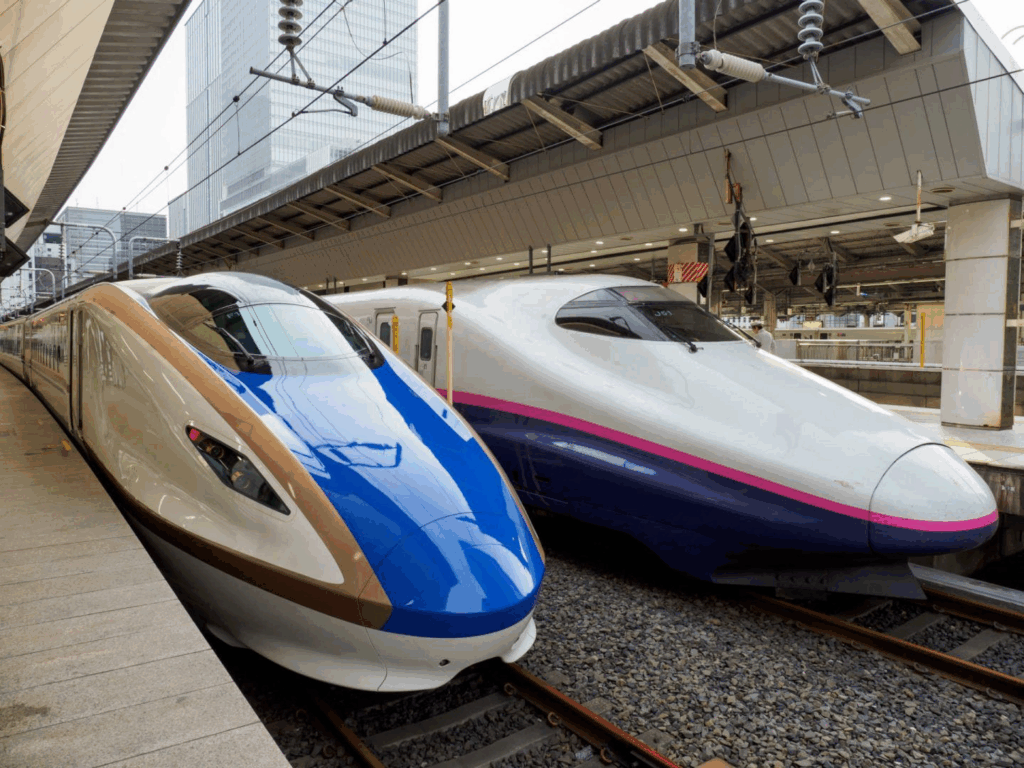

The NYC Subway vs. Advanced Train Systems: A Comparative Analysis
New York City’s subway system is an iconic part of the city’s infrastructure, serving millions of commuters daily. However, it faces numerous challenges, from outdated technology to frequent delays. In contrast, advanced train systems around the world, such as China’s bullet trains, Japan’s Shinkansen, and Europe’s high-speed rail networks, represent the pinnacle of modern rail technology. This blog will compare the NYC subway to these advanced systems, explore the pros and cons of renovating the subway, and discuss the implications for commuters.
NYC Subway: A Historical Perspective
The NYC subway system, one of the oldest in the world, began operations in 1904. Despite its age, it remains a vital part of the city’s transportation network. However, much of its technology dates back to the 1930s, including electromechanical relays and manual track switching. Efforts to modernize the system have included the introduction of communications-based train control (CBTC) on certain lines, which allows for more efficient train operations.
Advanced Train Systems: Cutting-Edge Technology
China’s Bullet Train: Developed rapidly since the mid-2000s, China’s bullet train system is the world’s largest and most advanced high-speed rail network. Utilizing electrical multiple unit (EMU) train sets, these trains can travel at speeds of up to 380 km/h (236 mph). The system includes the Shanghai Maglev, the world’s first high-speed commercial magnetic levitation line, which reaches speeds of 431 km/h (268 mph).
Japan’s Shinkansen: Known as the “bullet train,” Japan’s Shinkansen network is renowned for its speed, punctuality, and safety. Trains can travel at speeds of up to 320 km/h (200 mph), and the network covers major cities across Japan.
Europe’s High-Speed Rail: Europe boasts an extensive high-speed rail network, with trains like France’s TGV and Germany’s ICE reaching speeds of up to 300 km/h (186 mph). These systems emphasize connectivity between major cities and countries, offering efficient and comfortable travel options.
Pros and Cons of Renovating the NYC Subway
Pros:
- Improved Reliability: Modernizing signals and infrastructure can reduce delays and improve service reliability.
- Enhanced Safety: Upgrading outdated systems can enhance passenger safety, particularly in flood-prone areas.
- Better Commuter Experience: Renovations can lead to cleaner, more comfortable stations and trains.
Cons:
- High Costs: Renovating the subway system is expensive, with estimates reaching $43 billion over five years.
- Disruption: Construction and upgrades can cause significant disruptions to daily commutes.
- Long Timeline: Comprehensive renovations can take decades to complete.
Cost of Renovating the NYC Subway
The cost of renovating the NYC subway is substantial. The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) has outlined a $54 billion plan for improvements over the next five years. This includes modernizing signals, replacing aging subway cars, and upgrading infrastructure to withstand extreme weather. Specific projects, such as the renovation of Chambers Street and 190th Street stations, are expected to cost upwards of $100 million.
Impact on Commuters
Renovating the subway system will have mixed impacts on commuters. On the positive side, improved reliability and safety will enhance the overall commuting experience. However, fare hikes and service disruptions during construction may pose challenges. The introduction of modernized subway cars and expanded lines will ultimately benefit commuters by reducing overcrowding and improving access to underserved areas.
Fare Increases
As part of the financial plan to support these renovations, the MTA has proposed a fare hike that would raise the cost of a single ride to $3 by August 2025. While fare increases can be challenging for commuters, they are often necessary to fund essential upgrades and ensure the system remains safe and reliable.
Insurance Considerations
Insurance plays a crucial role in the renovation process. Flooding and other extreme weather events have exposed vulnerabilities in the subway’s infrastructure
Adequate insurance coverage is essential to mitigate risks associated with these events and ensure financial protection for both the MTA and commuters. Addressing insurance gaps and improving flood risk awareness are vital steps towards urban resilience
Is It Worth It?
The question of whether renovating the NYC subway is worth it depends on one’s perspective. From a long-term viewpoint, the benefits of a modern, reliable, and safe subway system outweigh the costs and disruptions. However, the immediate challenges, including high costs and construction-related inconveniences, cannot be ignored. Ultimately, investing in the subway’s future is crucial for maintaining New York City’s status as a global metropolis.
LEGAL DISCLAIMER: This communication is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Consult a qualified attorney for guidance on any legal matters.
Decisions should not be made solely based on this content without professional legal counsel. Individual circumstances vary, and only a personal attorney can determine applicability.
The views expressed are those of the individual creators and do not represent ASZ International, Inc. (dba ASZ Associates). Actions taken based on this content are at your own risk, and all liability is disclaimed.
This content is provided “as is” with no guarantees of accuracy, completeness, or reliability. Always verify information and seek legal advice as needed.